- Product Definition
Tungsten alloy disc is circular metal plates made primarily from high-percentage tungsten (typically 90–97%), alloyed with elements such as nickel (Ni), iron (Fe), or copper (Cu). They are manufactured through powder metallurgy, hot isostatic pressing (HIP), and precision machining processes. Based on thickness, they can be classified into thin discs, thick discs, and high-precision round plates.
- Key Performance Features
| Property | Description |
| High Density | Typically 17.0–18.8 g/cm³, allowing compact yet heavy design. |
| Excellent Mechanical Properties | High strength and hardness with outstanding impact and wear resistance. |
| Superior Thermal Stability | Maintains structural integrity under temperatures exceeding 2000°C. |
| Good Machinability | Supports precision turning, grinding, drilling, and polishing. |
| Outstanding Radiation Shielding | Highly effective against X-rays and gamma rays, superior to lead. |
| Environmentally Safe | Non-toxic and free of harmful radioactive elements; suitable for medical applications requiring high health standards. |
- Standard Specifications (Customizable)
Diameter Range: Φ5 mm to Φ300 mm (up to Φ500 mm for special requirements)
Thickness Range: 0.5 mm to 50 mm (thicker sizes available upon request)
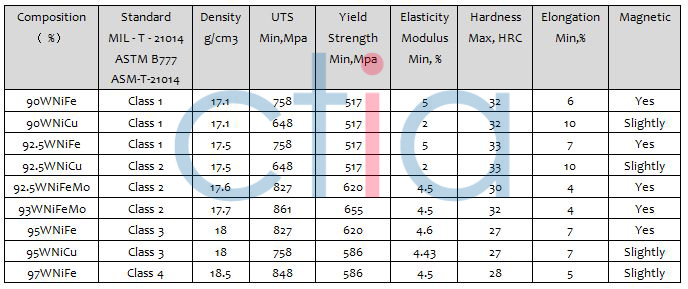
Density Grades: 17.0, 17.5, 18.0, 18.5 g/cm³, etc.
Surface Finish: Turned, ground, pickled, sandblasted, or polished
Tolerance Control: Diameter ±0.05 mm, thickness ±0.02 mm, or per drawing specifications
- Common Types
- Precision Balancing Discs – Used for dynamic balancing in aircraft, missiles, and gyroscopes.
- Medical Shielding Discs – Applied in radiation shielding for gamma knives, X-ray probes, and isotope containers.
- Electronic Heat Sink Discs – Employed for thermal management in power semiconductors and microwave devices.
- Armor-Piercing Military Discs – Serve as part of projectile cores or kinetic energy transfer structures.
- Mechanical Structural Discs – Used in ultra-hard molds, impact blocks, and inertial components.
- Typical Application Scenarios
| Industry | Application Examples |
| Aerospace | Satellite counterweights, flight control gyroscope discs, missile balancing plates |
| Medical Radiation Protection | Radiation source holders, isotope shielding shells, treatment probe bases |
| Electronics & Information | Heat sinks for high-frequency devices, RF thermal spreaders, microwave packaging pads |
| Defense & Military | Armor-piercing disc cores, explosion protection structures, precision flywheels |
| Industrial Precision Equipment | High-inertia rotating parts, stamping molds, anti-vibration base plates |
- Machining & Support Services
Support for custom design and non-standard shapes based on drawings
Capable of precision machining including drilling, tapping, chamfering, and slotting
Surface treatments available such as nickel plating, gold plating, passivation, etc.
Inspection reports provided upon request (density, dimensions, hardness, ultrasonic testing, etc.)
Available for both small-lot prototyping and volume production